How to operate a drone? It’s a question sparking increasing interest as these versatile machines become more accessible. From breathtaking aerial photography to precision surveying, drones offer a world of possibilities, but mastering their operation requires understanding safety protocols, technical skills, and legal considerations. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, equipping you with the knowledge to fly safely and effectively.
We will explore everything from pre-flight checks and essential controls to advanced flight modes and responsible drone operation. We’ll also cover crucial aspects such as photography tips, legal compliance, and troubleshooting common issues, ensuring you’re prepared for a successful and enjoyable drone experience.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for safe and successful drone operation. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, damage to the drone, and even injury. This section details the necessary steps and safety precautions to ensure a smooth flight.
Pre-Flight Inspection
Before each flight, a comprehensive inspection is essential. This involves checking the drone’s battery level, inspecting the propellers for damage, and verifying a strong GPS signal. Ensure the drone’s firmware is up-to-date and all components are securely attached. A visual inspection of the airframe for any cracks or damage is also recommended.
Safety Precautions
Safety is paramount in drone operation. Adhering to these precautions minimizes risks both to the drone and its surroundings.
| Pre-flight | During Flight | Post-flight | Emergency Procedures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Check battery level and charge. Inspect propellers and airframe for damage. Verify GPS signal. Plan flight path and avoid obstacles. | Maintain visual line of sight. Avoid flying near people or property. Respect airspace restrictions. Monitor battery level. | Power down the drone completely. Inspect for damage. Secure the drone and its components. Record flight data. | If GPS signal is lost, initiate Return-to-Home (RTH). If the drone malfunctions, attempt a controlled landing. If necessary, initiate emergency shutdown procedures. Contact emergency services if needed. |
Pre-Flight Checklist Flowchart

The following describes a visual representation of a pre-flight checklist and emergency procedures flowchart. The flowchart would begin with a “Start” node, branching into steps such as battery check, propeller inspection, GPS signal verification, and flight plan review. Each step would lead to a “Yes/No” decision point, with “Yes” proceeding to the next step and “No” leading to troubleshooting or corrective actions.
The flowchart would also include a separate branch for emergency procedures, such as loss of signal or malfunction, with steps to initiate RTH or emergency landing. The flowchart would conclude with a “Flight Complete” or “Emergency Resolved” node.
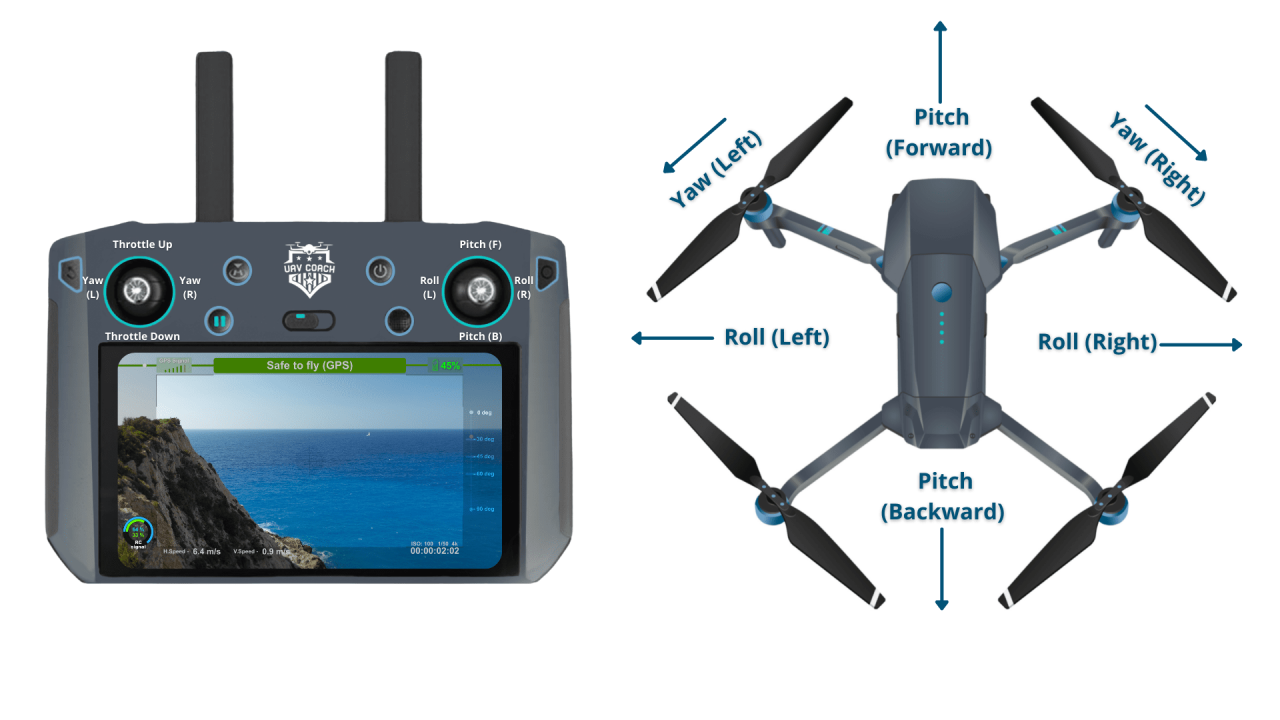
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Effective drone operation hinges on understanding and mastering its control system. This involves familiarity with different control interfaces, calibration procedures, and maneuvering techniques.
Drone Control Interfaces
Most drones utilize either joysticks or mobile app interfaces. Joysticks offer precise, real-time control, ideal for experienced pilots. Mobile apps provide a user-friendly interface, often with automated features, suitable for beginners. Each interface has its strengths and weaknesses; joysticks offer greater precision, while mobile apps offer ease of use and additional features.
Compass and GPS Calibration
Accurate compass and GPS calibration are vital for stable flight. Calibration involves following the manufacturer’s instructions, typically involving a series of movements to align the drone’s sensors with the Earth’s magnetic field and satellite signals. This ensures accurate positioning and prevents drifting or unexpected movements.
Takeoff, Landing, and Maneuvering
Proper takeoff, landing, and maneuvering techniques are essential for safe drone operation. Takeoff should be performed in a clear, open area, gradually increasing altitude. Landing should be slow and controlled, ensuring a gentle touchdown. Maneuvering requires smooth joystick inputs or app controls, adjusting speed and direction based on wind conditions and surrounding obstacles. In windy conditions, reduced speed and precise control are crucial.
In confined spaces, slow and deliberate movements are essential to avoid collisions.
Flight Modes and Features
Drones offer various flight modes, each designed for specific scenarios and skill levels. Understanding these modes and their features enhances control and safety.
Flight Mode Descriptions
Common flight modes include GPS mode (stabilized flight using GPS data), Atti mode (attitude mode, relying on onboard sensors), and Sport mode (increased responsiveness and speed, for experienced pilots). Each mode has its advantages and limitations, influencing stability, maneuverability, and ease of use.
Flight Mode Comparison

| Flight Mode | Key Characteristics | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS Mode | Stable flight, relies on GPS signal. | Easy to use, good for beginners, stable hovering. | Requires strong GPS signal, less responsive in GPS-denied environments. |
| Atti Mode | Relies on onboard sensors, less stable than GPS mode. | More responsive, works in GPS-denied environments. | Requires more piloting skill, can be less stable. |
| Sport Mode | Increased responsiveness and speed. | Faster maneuvers, dynamic shots. | Requires significant piloting skill, higher risk of accidents. |
Drone Features
Features like Return-to-Home (RTH), Follow Me, and waypoint navigation enhance drone functionality. RTH ensures the drone returns to its takeoff point automatically in case of signal loss or low battery. Follow Me mode allows the drone to follow a designated subject, while waypoint navigation enables pre-programmed flight paths.
Drone Photography and Videography: How To Operate A Drone
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning photos and videos. Mastering composition, camera settings, and filming techniques is crucial for high-quality results.
Shot Composition and Framing
Effective aerial photography and videography involves understanding composition rules like the rule of thirds and leading lines. Framing should be deliberate, considering the subject, background, and overall visual impact. Different angles and perspectives can drastically alter the mood and message of the captured content.
Camera Settings Adjustment
Adjusting camera settings such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture optimizes image quality in varying lighting conditions. Higher ISO values are useful in low light, but can introduce noise. Shutter speed affects motion blur; faster speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create motion blur. Aperture controls depth of field; wider apertures create shallow depth of field, blurring the background, while narrower apertures increase depth of field.
Capturing Smooth Footage
Smooth aerial footage requires careful piloting and potentially the use of image stabilization features. Smooth, deliberate movements and avoiding sudden changes in direction or altitude are crucial. Using a gimbal can significantly reduce vibrations and enhance image stability.
Best Practices
- Plan your shots beforehand.
- Utilize the drone’s features, such as RTH and waypoint navigation.
- Practice flying in various conditions.
- Always maintain visual line of sight.
- Edit your footage to enhance its quality.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly involves adhering to all relevant laws and regulations. This includes registration, permit requirements, and airspace restrictions.
Drone Regulations
Regulations vary by region, covering aspects such as registration, licensing, and airspace restrictions. Familiarize yourself with your local laws before operating a drone. These regulations often dictate where and when you can fly, and what activities are permitted.
Registration and Permits
In many jurisdictions, drone registration is mandatory. This involves providing identifying information about the drone and its owner. Specific permits may be required for commercial operations or flights in restricted airspace. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties.
Airspace Restrictions, How to operate a drone
Certain areas have restricted airspace, including airports, military bases, and national parks. Flying in these areas is illegal and can be dangerous. Consult online resources and apps to identify restricted airspace before each flight.
Legal Consequences
- Fines
- Drone confiscation
- Legal action
- Jail time (in severe cases)
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Even with careful operation, drones can encounter problems. Understanding common issues and their solutions ensures quick resolution and minimizes downtime.
Common Drone Problems
Common problems include low battery, GPS signal loss, motor malfunctions, and connectivity issues. Each problem requires a specific troubleshooting approach.
Troubleshooting Steps
Troubleshooting steps vary depending on the specific problem. For low battery, charge the battery fully. For GPS signal loss, relocate to an area with better signal. For motor malfunctions, inspect the motors for damage or obstructions. For connectivity issues, check the controller’s connection and the drone’s firmware.
Basic Drone Maintenance
Regular maintenance, such as cleaning propellers and inspecting the airframe, extends the drone’s lifespan and reduces the risk of malfunctions. Keep the drone clean and dry, and store it in a safe place away from extreme temperatures.
Troubleshooting Flowchart
A troubleshooting flowchart would start with identifying the problem. This would branch into different paths based on the specific issue (e.g., low battery, no GPS signal, motor failure). Each path would contain a series of steps to diagnose and resolve the problem, culminating in either a solution or a recommendation to seek professional assistance. The flowchart would utilize decision points and flow lines to guide the user through the process.
Drone Battery Management and Care
Proper battery management is crucial for optimal performance, safety, and longevity. This section details safe charging, storage, and maintenance practices.
Safe Charging Procedures
Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow the instructions carefully. Avoid overcharging, which can damage the battery. Charge the batteries in a well-ventilated area, away from flammable materials. Never leave batteries unattended while charging.
Battery Storage
Store drone batteries in a cool, dry place, away from extreme temperatures and direct sunlight. Avoid storing batteries at full charge for extended periods. Partially charged batteries (around 30-50%) have a longer lifespan.
Signs of a Failing Battery
Signs of a failing battery include reduced flight time, inconsistent performance, and unusual swelling or heat generation. If you notice any of these signs, replace the battery immediately.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, safe and responsible drone operation is paramount for both the operator and the surrounding environment.
Extending Battery Lifespan
To extend battery lifespan, avoid deep discharges, store batteries properly, and avoid extreme temperatures. Use a balance charger to ensure all cells in the battery are charged evenly.
Successfully operating a drone involves a blend of technical proficiency and responsible decision-making. By diligently following pre-flight checklists, understanding drone controls, and adhering to all safety and legal regulations, you can unlock the full potential of your drone while ensuring the safety of yourself and others. Remember, continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a skilled and confident drone pilot.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning to safely and effectively pilot your drone is crucial, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone. This guide will help you confidently navigate the complexities of drone flight, ensuring a safe and successful experience.
Proper operation is paramount for responsible drone use.
Embrace the journey of discovery and enjoy the remarkable perspectives that await you.
Q&A
What is the ideal wind speed for safe drone operation?
Generally, wind speeds below 15 mph are considered safe for most drones. However, always check your drone’s manufacturer specifications for wind tolerance limits.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass and GPS?
Calibrating before each flight is recommended, especially if you’re operating in a new location or after a significant impact. Your drone’s manual will provide specific instructions.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If GPS is lost, activate RTH immediately and monitor the drone’s descent. If RTH fails, prepare for a manual landing.
How long does a typical drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes on average, but always consult your drone’s specifications.